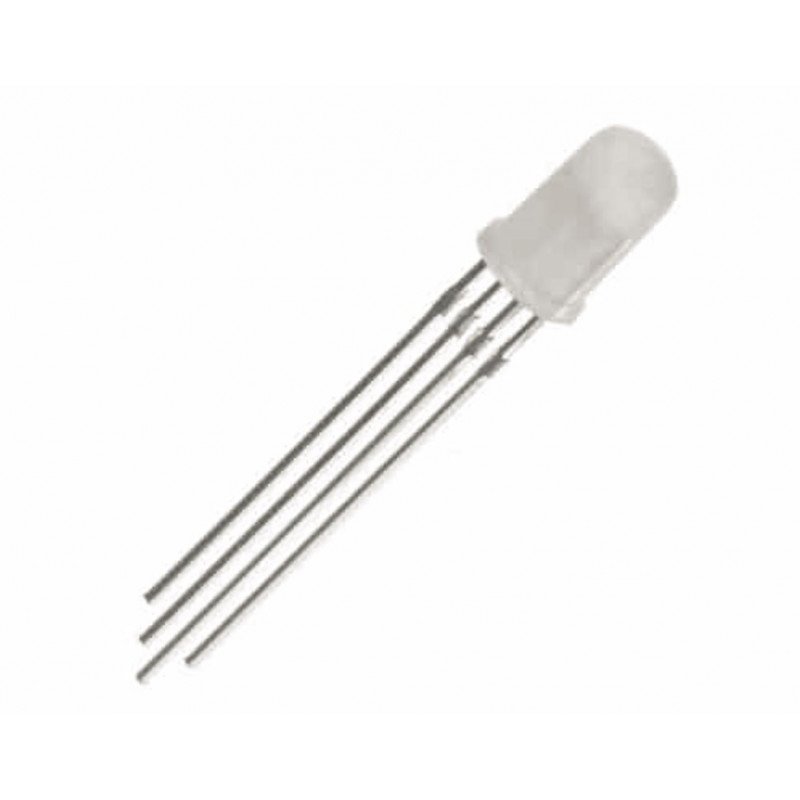
A Light-Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor-based light source that emits light when an electric current passes through it. During this process, electrons recombine with holes within the material, releasing energy as photons. The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor’s bandgap energy. To produce white light, manufacturers either combine multiple LEDs of different colors or coat the LED with a phosphor layer that converts the emitted light into a broad-spectrum white glow. This efficient and versatile technology is widely used in indicators, displays, and general lighting applications due to its brightness, durability, and low energy consumption.
-
 Power-supply
Power-supply
-
 Electronic components
Electronic components
-
 Boards & Programmer
Boards & Programmer
-
 Electromechanical
Electromechanical
-
 Tools
Tools
-
 Quadcopter and Drone
Quadcopter and Drone
-
 Wires
Wires
-
 Switches
Switches
-
 Magnets
Magnets
-
 Heat Shrink Tube
Heat Shrink Tube
-
 Connectors
Connectors
-
 Cooling Fans and Acessories
Cooling Fans and Acessories
-
 Sensors & Module
Sensors & Module
-
 IOT & Wireless Boards
IOT & Wireless Boards
-
 3D Printer
3D Printer
-
 Displays and Accessories
Displays and Accessories
- Home
- Displays and Accessories
- LCD and LED Displays
- RGB LED - 5mm - Common Anode
RGB LED - 5mm - Common Anode
In stock
Out of stock
A Light-Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current flows through it. Electrons recombine with holes, releasing energy as photons. The light’s color depends on the bandgap energy. White light is achieved using multiple LEDs or phosphor coatings. LEDs offer efficiency, durability, and versatility.
GST:
Total Price:
Buy minimum
Quantity and get
extra discount!
| Filename | Size | Type | Downloads |
|---|
Be the first one to review this product.
- ...
- ...

